
After a point, specialised cells begin to form for specific tasks.Īnd soon a complete organism forms and is ready to be born. Once there is a sufficient mass of cells to create a hollow ball (blastula), it folds in to expand exponentially. In addition, the zygote multiplies from one to two, to four, and so on. However, to grow and develop, the zygote needs more cells. In multi-celled Eukaryotes, the male and female gametes combine to form the zygote- the building block of a new life. In mitosis, development is the primary function. Functions of Meiosis vs Mitosis Meiosis vs Mitosis: Development Mitosis takes place in several stages after the replication of DNA. And in multi-cell Eukaryotes, the zygote form after conception transforms into a fully formed organism via mitosis. In single-cell Eukaryotes, mitosis is the basis of asexual reproduction. Further, during the process, its DNA replicates. In the cell cycle, mitosis is a process, in which a cell split into two new cells. Read below to have a complete idea of the processes of meiosis vs mitosis. The two main ways of cell division are Mitosis and Meiosis. But to keep life going, cells must multiply, to heal or reproduce. Whether it is a single-cell organism or a multicellular one. Microtubules from one centrosome attach to the kinetochore (protein structures at the centromeres) of one chromosome from each of the homologous pairs, while the other centrosome connects to the kinetochore of the other chromosome in each homologous pair, and each homologous pair moves towards the metaphase plate (where they line up before anaphase).1.11 Solved Question for You Meiosis vs MitosisĬells are the building blocks of life. Centrosomes move to opposite ends of the cell, and the nuclear envelope dissolves.ħ.

This formation occurs because of sister chromatid cohesion, where a gene that has been given to the homologous pair in synapsis is still bonded to the corresponding part on the sister chromatid of its former chromatid.Ħ. Some of these homologs have one or more chiasmata, an X shaped region where a genetic rearrangement has occurred. Synapsis ends, and the homologs move slightly apart, no longer bonded along their lengths like in the synaptonemal complex.ĥ. This forms a synaptonemal complex.ģ.The random rearrangement of corresponding genes occurs between the non sister chromatids (because at this stage each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids).Ĥ.
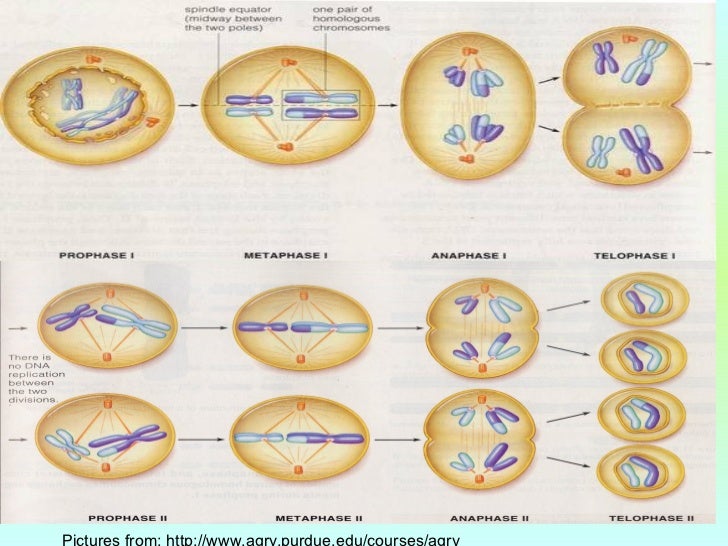

The paired homologs become physically connected along their lengths through a process called synapsis. Chromosomes condense and homologs loosely pair along their lengths, aligned by gene.Ģ.
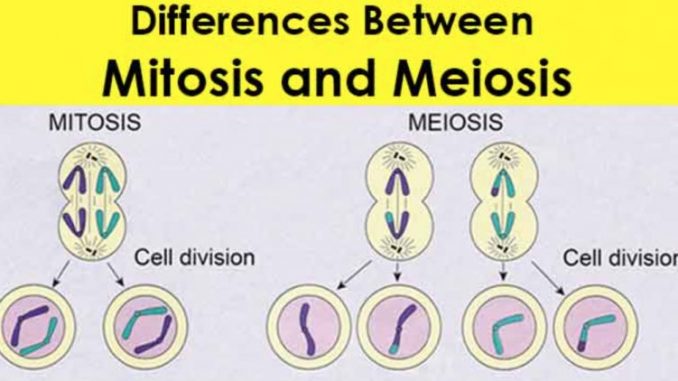
The above is also how a 46 chromosome (double strand) cell in mitosis can result in 2 daughter cells each with 46 chromosomes (single strand).Įven Sal admits how confusing this is, but he explains all this visually in a separate video differentiating the terms chromatid, chromosome, and chromatin.ġ. So a haploid parent cell of 23 chromosomes (double strand) just created two haploid daughter cells of 23 chromosomes (now single strand). When the chromatids are separated they are now called chromosomes Anaphase II splits the sister chromatids which now separate (23 chromatids go to one pole and 23 chromatids go to other pole). The parent cell starts with 23 chromosomes (EACH double stranded=two sister chromatids, so there are 46 chromatids. This means that in meoisis II when we split the sister chromatids: It is only when the sister chromatids separate are they each considered separate chromosomes. The single strand chromosome (1 chromosome) became two stranded yet attached identical sister chromatids (still 1 chromosome) Likewise chromosome 5 of dad is similar to chromosome 5 of mom)Īfter replication how many chromosomes do we have?
Prophase of mitosis vs meiosis code#
In interphase before S (replication phase) we have 46 single stranded chromosomes: 23 are from mom and 23 are from dad (they code for the same things meaning chromosome 1 of mom codes for the same thing as chromosome 1 of dad. Remember that when replicating in interphase, the chromosome number DOES NOT CHANGE


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
